Schematic drawing of a nephron. Illustration printed with permission... Download Scientific

Kidney Microanatomy (Lesson) Human Bio Media
1/4. Synonyms: Cortex renalis. The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. The nephron is the main functional unit of the kidney, in charge of removing metabolic waste and excess water from the blood.

Schematic drawing of a nephron. Illustration printed with permission... Download Scientific
2. The "Bowman's capsule" is the part of a nephron which receives the filtrate. It is a part of a nephron, and only delivers filtrate to a single nephron. The afferent artery and efferent artery are not nephrons, they are arteries outside the nephron that run around the kidney (the red lines that run around the large kidney diagram to the right.
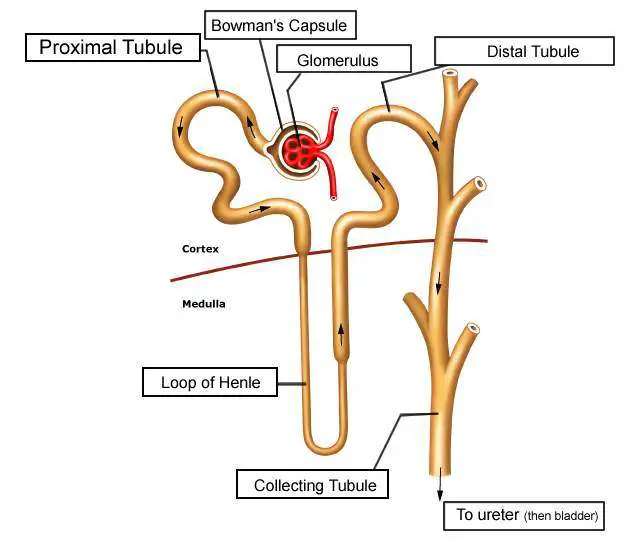
Diagram of nephron Healthiack
This video tutorial demonstrates how to draw Nephron step by step. You can learn how to draw and label the parts of Nephron diagram, just watching this vide.

How To Draw Structure Of Nephron Diagram Step By Step For Beginners YouTube
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen.

How To Draw Nephron step by step for beginners YouTube
How to draw nephron in easy steps : Life Processes | CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus | Biology | NCERT 10th Class | Best Animated video Lectures | grade boost.

File Kidney Nephron Molar Transport Diagram Png Wikimedia Commons Gambaran
Diagram of the Nephron, Glomerulus and Different Parts of the Tubule. The tubules are lined with a thin layer of epithelial cells. The thinner segments of the tubules like the descending limb and first part of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle has cells with minimal organelles. The other segments have thicker cells with a brush border and.

The Urinary System Nephron and Urine Formation Owlcation
The purpose of this study is to see whether a large drawing of a nephron helped medical students in self-directed learning groups learn renal physiology, histology, and pharmacology before discussing clinical cases. The end points were the grades on the renal examination and a student survey. The classes in the fall of 2014 and 2015 used the drawing, but not those of 2012 and 2013. The Charles.

Structure Of A Nephron Formation Of The Urine Stock Illustration Download Image Now Nephron
A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed, and excreting the rest as urine. Its function is vital for homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, and plasma osmolarity. It is regulated by the neuroendocrine.

How to draw easy diagram of nephron step by step for beginners YouTube
Each nephron has basically two parts.. 'Nephron Diagram || How to draw and label the parts of a Nephron' is demonstrated in this video tutorial step by step.
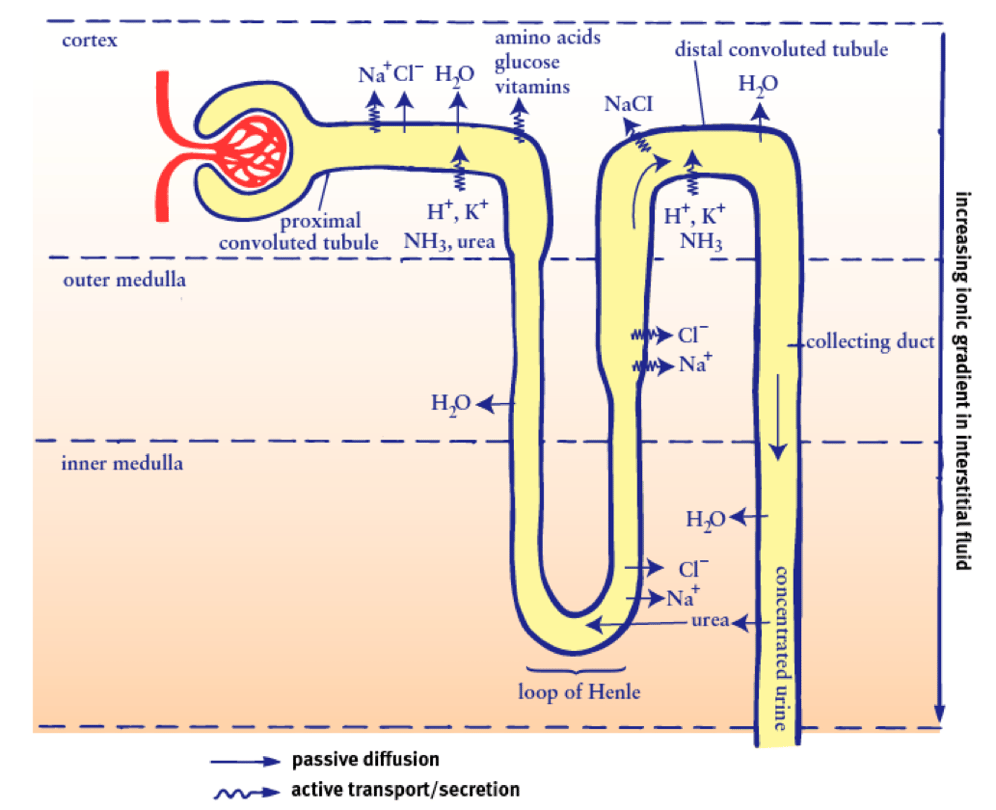
CC Breaking down nephron functioning into six easy steps!
The purpose of this study is to see whether a large drawing of a nephron helped medical students in self-directed learning groups learn renal physiology, histology, and pharmacology before discussing clinical cases. The end points were the grades on the renal examination and a student survey. The classes in the fall of 2014 and 2015 used the.
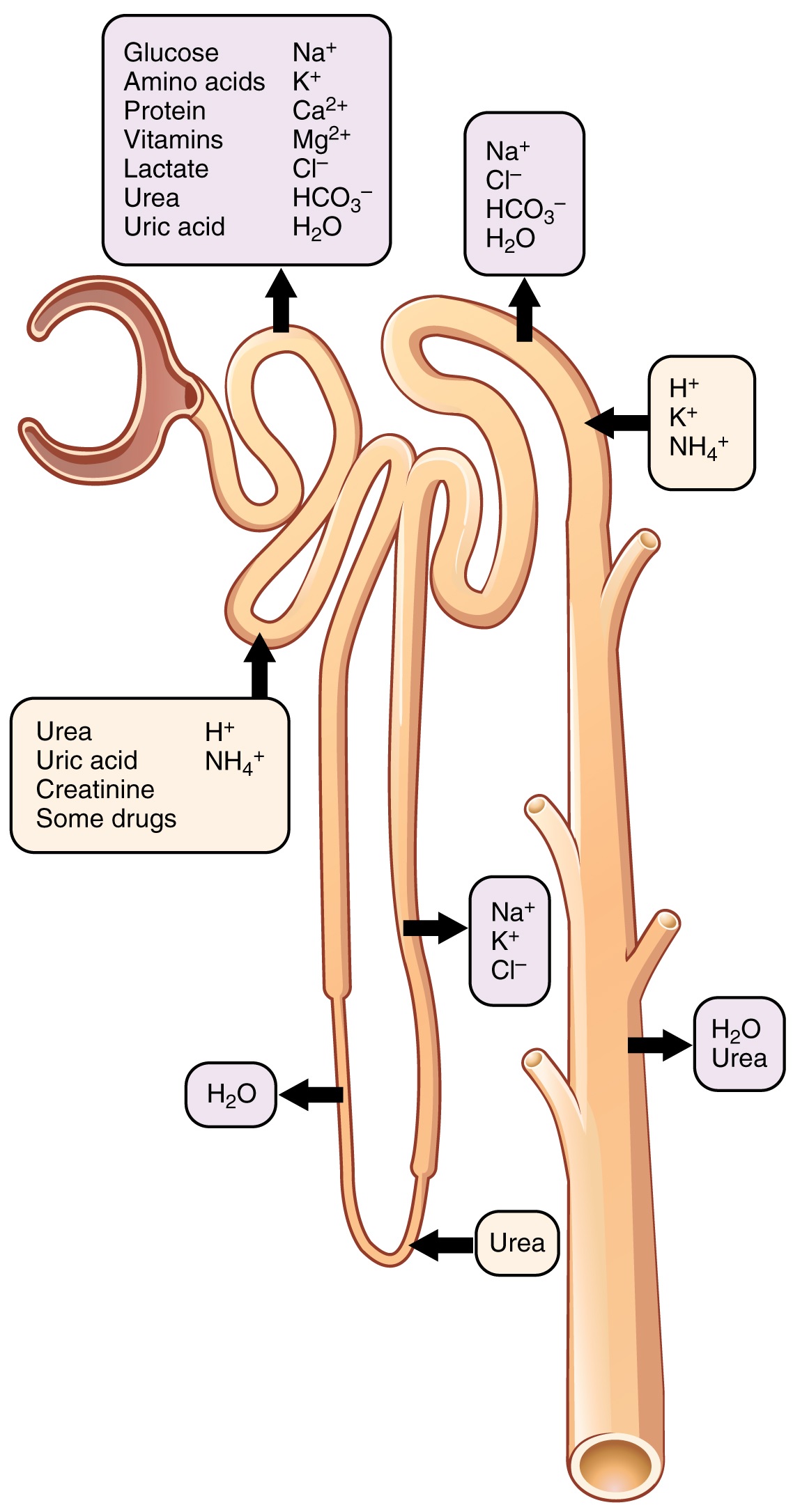
Structure and Functions of Nephron
Structure of Nephron. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 35-55 mm long. At one end, the tube is closed, folded and expanded, into a double-walled, a cuplike structure called the Bowman's capsule or renal corpuscular capsule, which encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels called the glomerulus.

Nephron Definition, Structure, Physiology, Functions
Below is a well-labelled and easy diagram of the nephron for your better understanding. Broadly, a nephron can be divided into two parts - renal corpuscle and renal tubule. The renal corpuscle is the filtering component and renal tubules carry the filtered liquid away. A human nephron is a long fine tubule that is about 30-55 mm long.
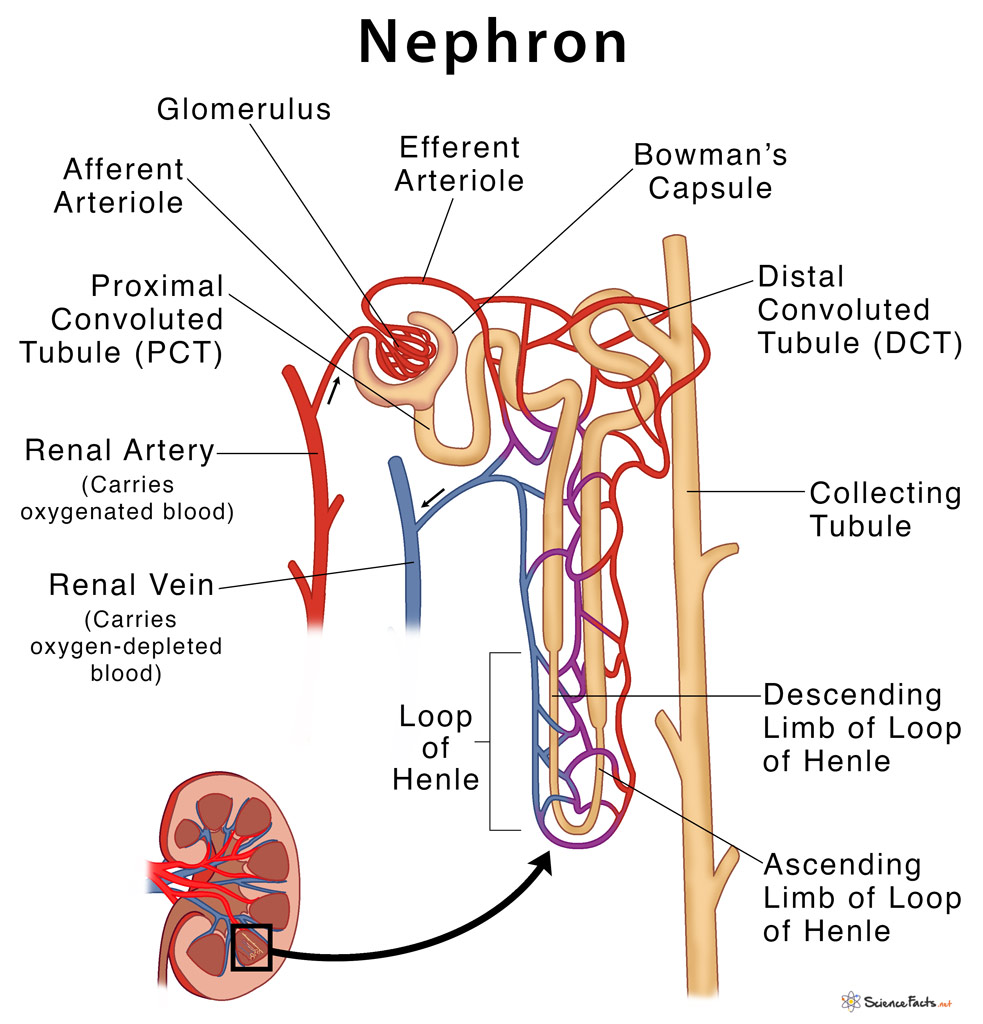
Nephron Definition, Parts, Structure, & Functions, with Diagram
A nephron is the basic unit of structure in the kidney. A nephron is used separate to water, ions and small molecules from the blood, filter out wastes and toxins, and return needed molecules to the blood. The nephron functions through ultrafiltration. Ultrafiltration occurs when blood pressure forces water and other small molecules through.

Simple Diagram Of Nephron
nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. The most primitive nephrons are found in the kidneys ( pronephros) of primitive fish, amphibian larvae, and embryos of more advanced.
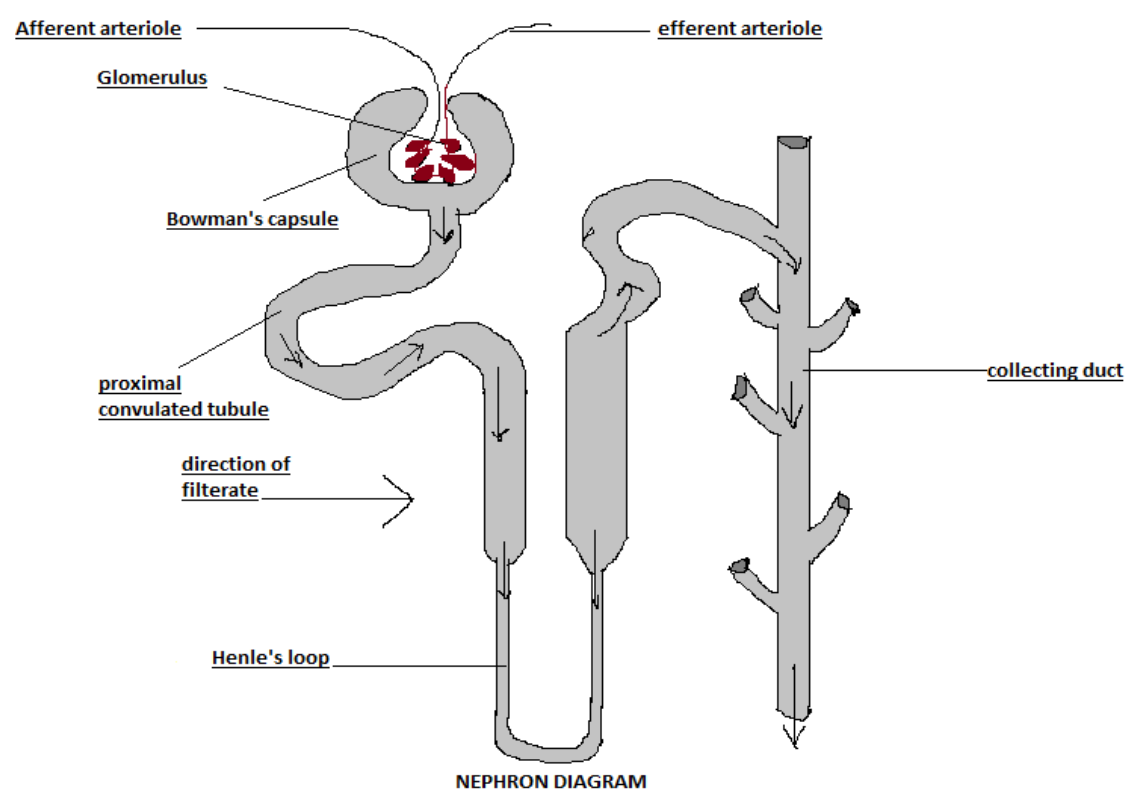
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structure.
Nephron (overview) Ultrastructurally, the nephron is the functional representative of the kidney. Each nephron contains arenal corpuscle, which is the initial component that filters the blood, and a renal tubule that processes and carries the filtered fluid to the system of calyces. The renal corpuscle has two components: the glomerular (Bowman.

Diagram of the nephron segments and its juxtaglomerular apparatus Download Scientific Diagram
A nephron is the unit of structure and function in the kidney. Each nephron is a coiled tube held together by a tough fibrous connective tissue. In humans, a healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney, functioning together to filter blood from all its impurities. They also regulate blood pressure, control electrolytes, and.